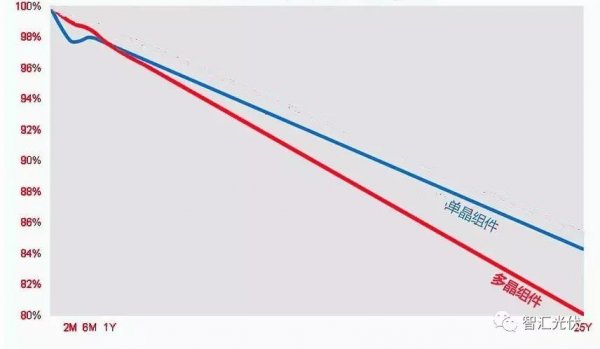
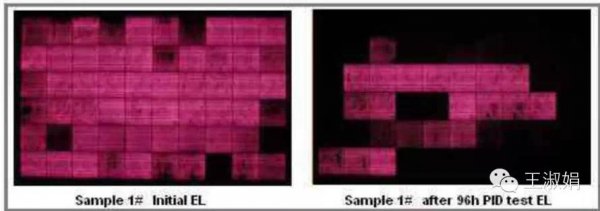
1. The concept of photovoltaic module attenuation Photovoltaic module attenuation rate means: The ratio of the output power to the nominal power of the PV module after running for a period of time under standard test conditions (AM 1.5, module temperature 25°C, irradiance 1000 W/m 2 ). According to national regulations: Monocrystalline silicon modules do not attenuate more than 3% in the first year, and polycrystalline silicon modules do not attenuate more than 2.5% in the first year, and do not exceed 0.7% per year thereafter. 2, the type of attenuation The attenuation is generally divided into initial photo-attenuation and aging decay. In addition, PID potential induced decay has also been recognized in recent years. 1) Light Induced Degradation (LID) The essential reason for LID generation is that solar cells generate recombination centers inside the material after receiving light. At present, it is generally accepted that the boron-oxygen complex produced after illumination reduces the lifespan of the child. Depletion of Boron in the boron-doped crystalline silicon and deeper energy defects excited by the interstitial oxygen under light irradiation cause carrier recombination and cell performance deterioration, resulting in a sharper output power of the PV module in the initial application for several days. Decline, but after a period of time (usually 2 to 3 months) the output power will gradually stabilize. 2) Aging decay The slow decay that occurs in the long-term application of photovoltaic modules can be divided into two categories: 1) The attenuation caused by the aging of the battery itself is mainly affected by the production process of the battery type (single crystal, polycrystalline) and the battery; 2) The attenuation caused by the aging of the packaging material is positively related to the production process and packaging materials of the photovoltaic modules and the environment of the components. Common cracking, yellowing of the appearance, wind and sand wear, hot spots, and aging of the components all can accelerate the power attenuation of the components. 3) PID potential induced attenuation This attenuation exists in the high voltage between the component's internal circuitry and its grounded metal bezel, which can cause power degradation of the component, and is also related to glass, backplane, EVA, temperature, humidity, and voltage. The attenuation of the conventional components is shown in the figure below. In the figure, the blue line is the attenuation curve of the monocrystalline silicon device, and the red line is the attenuation curve of the polysilicon device. among them: Due to the LID effect of the monocrystalline silicon module, the power of the photovoltaic module drops rapidly within 2 months and recovers slowly in the later period. The polysilicon component also has a LID effect but results in significantly lower attenuation than single crystals. For more than one year, the power is mainly reduced due to aging decay. The following figure shows the infrared photo of the PID effect. The cells with serious PID effect are blackened. The PID effect causes a significant drop in the power of the component. Facial Lock,Facial Recognition System,Face Scanner,Facial Recognition Search ChangChun E-vida Technology Co.,ltd , https://www.evidatech.com