Magnesium alloy has become a new type of medical metal material with great clinical application prospect because of its good biocompatibility, mechanical properties matching with bone tissue, and the ability to be degraded and absorbed in human body. The biomaterials research team led by Yang Ke, a researcher at the Institute of Metal Research at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed a new concept of biofunctionalization of medical metal materials in recent years. Its core idea is to enable medical metal materials to exert their own excellent mechanical properties while also possessing Specific biomedical features to achieve better clinical outcomes. Based on this idea, the Yang Ke team successfully developed a new type of degradable magnesium-copper binary alloy with multiple biomedical functions in recent years. Yang Ke’s recent research work led by Dr. Liu Chen, a doctoral student who has been instructed by Yang Ke, showed that the use of magnesium-copper alloy in the physiological environment to degrade the alkaline environment and the sustained release of magnesium and copper ions has given the new type of degradable magnesium alloy to be antibacterial and facilitated. Bone, promote vascularization and other multiple biomedical functions, and ensure its bio-safety and mechanical support role, great clinical application value. Copper is an important trace element in human tissues, which regulates the metabolism of human body and the functions of various enzymes. Copper promotes hematopoietic function, regulates the absorption and utilization of iron, maintains the normal functions of bones, blood vessels, skin, and endocrine, and promotes the production of bone, blood vessels, and skin collagen. Lack of copper can affect the body's secretion system and immune function, leading to anemia, thrombosis, coronary arteriosclerosis, arthritis, osteoporosis and other diseases. The strong antibacterial effect of copper has been recognized and used for a long time. It is the only solid material that has obtained EPA antibacterial registration. Copper can long-term inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, and has a highly effective killing effect against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Candida albicans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria. Based on the degradable characteristics of magnesium metal in the biological environment and the numerous biological functions of copper, the Yang Ke team researched and developed a magnesium-copper binary alloy with multiple biomedical functions and applied for a Chinese invention patent. Studies have shown that magnesium and copper alloys continuously dissolve magnesium ions and copper ions during the degradation process, but the dissolution rate is within the range that the human body can tolerate. Therefore, it does not affect the biological safety. The results of hemolysis and cytotoxicity experiments showed that magnesium-copper alloy has good blood compatibility and cell compatibility. The results of antibacterial experiments showed that Mg-Cu alloys had a dual antibacterial effect on S. aureus with a combination of alkaline antibacterial and copper-ion antibacterial, showing more excellent antibacterial function (see Figure 1). In addition, magnesium-copper alloy also has obvious contributing bone formation (see Figure 2) and vascularization (see Figure 3). The research of new biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with multiple biological functions has realized the integration of biodegradable magnesium alloy structure and biomedical function, which helps to solve the problems caused by implant materials in clinical infections and enables the degradable magnesium alloys to play a role. Greater clinical treatment provides doctors and patients with better choices, and also provides strong support for the extensive clinical application of biodegradable magnesium alloys. Related research results have been published online recently in Scientific Reports (Chen Liu, Xuekun Fu, Haobo Pan, Peng Wan, Lei Wang, Lili Tan, Kehong Wang, Ying Zhao, Ke Yang, Paul K. Chu. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys With enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects, 2016, DOI: 10.1038/srep27374). 1. Technical standard: BS EN 10202, DIN EN 10203, GB/T2520 , JIS G3303 Hot-Melting Laminated Tinplate Hot-Melting Laminated Tinplate,Tinplate Cold Rolled Steel,Tinplate Ppgi And Aluminum,Tin Plate Jiangsu Guolian New Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.cntinplate.com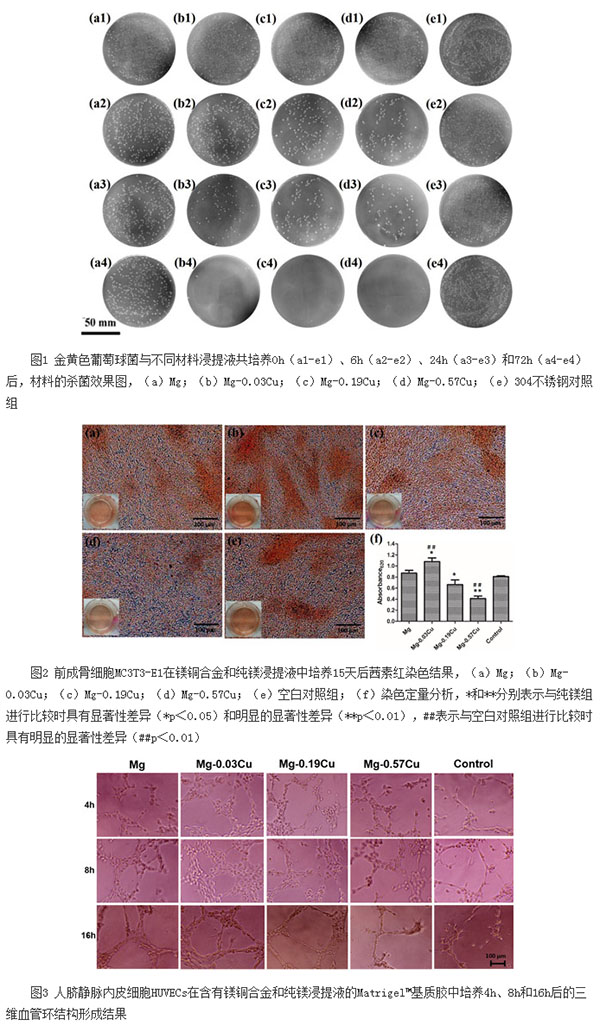
2. Steel type: MR, SPCC
3. Thickness: 0.115 - 0.50 mm
4. Width: 600 - 1050 mm
5. Length: 600-1200mm
Tin Coating: ordinary 2.8 or 2.8g and 5.6g or 5.6g, we can produce according to customer's requests
substitute whitel lacquering
Environmentally friendly production
Excellent barrier property
Excellent processability
short delivery time & save freight cost