With the development of computer bus technology, computers play an increasingly important role in the field of measurement and control. The computer bus has evolved from the initial low-speed ISA bus to the 133M PCI bus to the 10G bandwidth PCI-Epress bus. The "data transmission bus bottleneck" for high-speed acquisition has gradually been resolved. The USB series module is a data acquisition module developed by Advantech Co., Ltd., including complete A/D, D/A, DIO, USB to serial port, USB Hub and other products. It adopts USB2.0 standard and carries out rugged industrial design in various fields. There are more applications. Hot Stamping Foil,Hot Foil Stamping Machine ,Foil Stamping ,Foil Printing Aluminum Sheet Co., Ltd. , http://www.nbaluminumcoil.com
On the other hand, the development of Ethernet technology, the transmission rate from 10M to 1G, the network-based distribution has been rapidly developed, but the Ethernet acquisition module can not achieve PCI bus interrupt and DMA response function, to achieve high-speed acquisition also needs The acquisition module has a CPU or the like. Measurement Bus VXI/PXI/LXI technology can achieve high speed acquisition, synchronous triggering and hot swapping, but it is expensive.
The emergence of the USB bus just solves this problem. The purpose of the Universal Serial Bus Architecture (USB) developed by Intel was originally to consider the connection between the computer and the telephone, the ease of use of the device, and the port expansion, and is currently applied to various fields. The speed from 11M to 2.0Mbps of USB2.0 has exceeded 100Migabit Ethernet, and it has bus power supply, hot swap, interrupt function, etc., and has low cost and open architecture, and is widely used in general measurement fields.
USB specification USB transmission signal and power supply through a four-wire cable, two power lines (V-bus / GND) use +5V power supply, two signal lines (D + / D-), long and short pins can guarantee The security during hot plugging, while the USB specification has developed the "power management" function, the system software can be combined with the host's energy management system to handle various power components such as suspend, wake up, and distinctively, USB devices Application-specific power management features allow system software to control power management and automatically identify USB devices. The latest USB 2.0 specification supports a transfer rate of 480M, which is extracted from the PCI Express IO bridge to ensure high-speed transmission.
USB bus layout technology
The USB device is connected to the USB device and the USB host. The physical connection of the USB is a hierarchical star structure. Each hub is at the center of the star, and each segment is a point-to-point connection. From the host to the hub or its features, or from the hub to the hub or its features, the USB topology can be seen in the figure. The USB specification stipulates that up to 127 peripherals can be dialed up to six layers by using the Hub extension. The standard USB cable length is 5m, and the peripheral distance can reach 30m (65) through the Hub or Repeater. In recent years, a "USB extender" technology has been introduced that extends USB to 100M by using Category 5 cable. This technology extends the flexibility of USB measurement systems, but for high speed and accurate measurement systems. Further testing is not required and is not included in the specification. 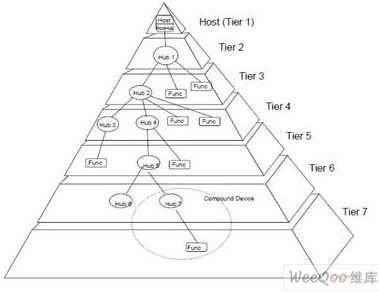
USB data transfer type
USB defines four transfer types:
Control Transfer: A reliable, aperiodic, host-initiated request or response transfer, typically used for command transactions and state transactions.
Synchronous transfer: Periodic, continuous communication between a host and a device, typically used to transfer time-related information. This type preserves the ability to include time concepts in the data. But this does not mean that the time to transmit such data is always important, that is, the transmission is not necessarily urgent.
Interrupt transmission: low-speed, fixed-delay transmission of small-scale data.
Batch transfer: non-periodic, reliable delivery of large packages. Typically used to transmit data that can utilize any bandwidth, and this data can tolerate waiting when there is no available bandwidth. 
Through the above mechanism, the USB device can be guaranteed to transmit at a high speed while ensuring correctness.
USB data acquisition module design

Take the USB-4718 8-channel thermocouple input module as an example. The schematic diagram is as follows: 
The differential signal enters the A/D converter through the multi-way selection switch, and the converted digital signal is connected to the USB Host of the computer through the USB interface chip. The schematic diagram of the A/ conversion is as follows: 
While providing hardware products, Advantech provides drivers for Windows, WinCE, Linux and other operating systems. Not only can you use VC, VB, Delphi and other high-level languages ​​for development, but you can also apply it to Labview software through the driver interface.
ActiveDAQ Pro is a new graphical measurement component developed by Advantech. It uses the Advantech data acquisition card driver and ActiveDAQ Pro to encapsulate the complex development process, presenting users with extremely powerful functions, stable performance and simple application development. This also reflects the improvement of the mature product company's product flow.
The following is an example of a virtual multimeter developed using the Advantech USB-4718 8-channel thermocouple input module, device driver, and ActiveDAQ Pro. It can realize all the functions of the multimeter and the interface is beautiful. It also includes temperature measurement, curve display, data logging and communication functions that are not available in ordinary multimeters. 